Have a question about the ONC Health IT Certification Program or operations? Review our list of Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) below. If you have a specific question about ONC regulations, you should also visit our regulatory FAQs.
Jump To:
- A. Overview
- B. Certification
- B1. How is a Health IT Module certified?
- B2. What is the role of the ONC-Approved Accreditor (ONC-AA), and how is the ONC-AA chosen?
- B3. What is the role of ONC-Authorized Certification Bodies (ONC-ACBs) in the ONC Health IT Certification Program and how do organizations apply to become an ONC-ACB?
- B4. What rules do ONC-ACBs have to follow, and where can I find a list of ONC-Authorized Certification Bodies (ONC-ACBs)?
- B5. How long does an ONC-ACB’s status last, and how do ONC-ACBs renew their status?
- B6. How can I submit a Health IT related complaint?
- B7. What does the ONC Certified HIT Certification and Design Mark represent?
- B8. What is gap certification?
- B9. What happens to Health IT modules when new standards and certification criteria are released?
- B10. What is inherited certification status?
- B11. How does inherited certification status work?
- B12. How does inherited certification status work for EHR modules?
- B13. How does privacy and security certification work for Health IT Module certification?
- C. Testing
- C1. Where can I find the ONC-Approved Test Method?
- C2. What is the role of the National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program (NVLAP)?
- C3. What is the role of Accredited Testing Laboratories (ATLs) in the ONC Health IT Certification Program, and how do organizations apply to become an ATL?
- C4. Where can I find a list of Accredited Testing Laboratories (ATLs)?
- C5. Are code sets available in the ONC Health IT Certification Program?
- D. Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL)
- D1. What is the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL), and where can I find a list of Health IT modules?
- D2. How do I use the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL) and obtain a CMS EHR Certification ID?
- D3. How can I check that the EHR product that I’m using is certified, and how often is the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL) updated?
- D4. What do I do if I do not see my EHR product on the CHPL?
- D5. What does "Additional Software Required" mean?
- D6. What is the difference between a Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL) Product Number and a CMS EHR Certification ID?
- D7. How do I get my Health IT Module listed on the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL)?
- D8. Who do I contact with questions or concerns about the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL) or if my CHPL listing is incorrect?
- E. Complaints and Violations
A. Overview
A1. How is the ONC Health IT Certification Program structured?
The graphic below depicts the ONC Health IT Certification Program. ONC manages the overall program.
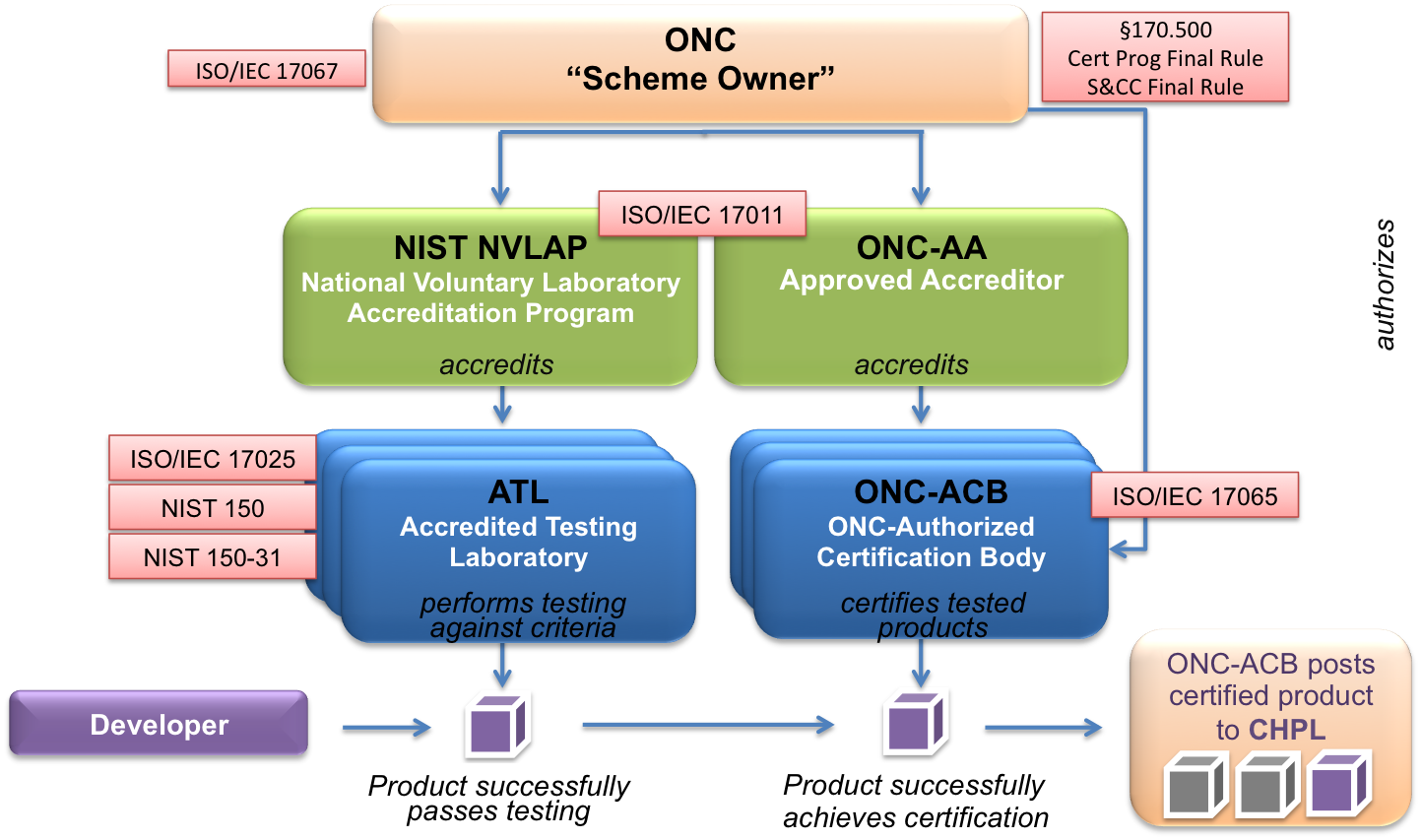
The ONC-Approved Accreditor (ONC-AA) accredits and oversees certification bodies. Accredited certification bodies must seek authorization from ONC to participate in the ONC Health IT Certification Program - once authorized, they are called ONC-Authorized Certification Bodies (ONC-ACBs).
NVLAP is the accreditor for testing laboratories in the ONC HIT Certification Program. NVLAP is responsible for accrediting and overseeing Accredited Testing Laboratories (ATLs).
A single organization can serve as both an ONC-ACB and an ATL, as long as a firewall is established between testing and certification activities.
Developers or Vendors have their Health IT Module(s) tested by an ATL. After the Health IT Module has been successfully tested, it can be certified by an ONC-ACB. Products certified by an ONC-ACB are posted to the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL).
A2. What if I have questions about the CMS EHR Incentive Programs?
Learn more about Meaningful Use (MU) and the CMS EHR Incentive Program
B. Certification
B1. How is a Health IT Module certified?
Developers and Vendors wishing to certify a Health IT Module(s) first contacts an Accredited Testing Laboratory (ATL) to have their product tested. Once their product is determined to satisfy all applicable certification criteria adopted by the Secretary, the Developer or Vendor then contacts an ONC-Authorized Certification Body (ONC-ACB) to have their product certified.
B2. What is the role of the ONC-Approved Accreditor (ONC-AA), and how is the ONC-AA chosen?
The National Coordinator will publish a notice in the Federal Register to announce the period during which organizations may submit requests for ONC-AA status. An organization must submit a timely request in writing to the National Coordinator which includes the information required at §170.503 and §170.504 of the Establishment of the Permanent Certification Program Final Rule [PDF - 534 KB].
In June 2011, ANSI was selected as the first ONC-AA; effective June 2014, ANSI started their second 3-year term as the ONC- Approved Accreditor.
B3. What is the role of ONC-Authorized Certification Bodies (ONC-ACBs) in the ONC Health IT Certification Program and how do organizations apply to become an ONC-ACB?
ONC-ACBs certify Health IT Modules have been successfully tested by an Accredited Testing Laboratory (ATL) against the certification criteria adopted by the Secretary. ONC-ACBs submit certified Health IT Modules for posting on the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL).
An organization seeking to apply to become an ONC-ACB must submit an application to the ONC-Approved Accreditor (ONC-AA) to seek accreditation. Contact information for the ONC-AA can be found here.
Once the organization is accredited, they must apply to ONC to become an ONC-ACB. An application for ONC-ACB status may be submitted to the National Coordinator at any time.
The application process is highlighted in the Establishment of the Permanent Certification Program for Health Information Technology [PDF - 534 KB] in sections 170.525, 170.530, and 170.535.
Additional instructions can be found here.
B4. What rules do ONC-ACBs have to follow, and where can I find a list of ONC-Authorized Certification Bodies (ONC-ACBs)?
The Principles of Proper Conduct for ONC-ACBs are detailed in 170.523 of the Establishment of the Permanent Certification Program for Health Information Technology [PDF - 534 KB]. A list of the ONC-ACBs is available here.
An ONC-ACB must provide remote certification for both development and deployment sites.
B5. How long does an ONC-ACB’s status last, and how do ONC-ACBs renew their status?
An ONC-ACB's status will expire three years from the date it was granted by the National Coordinator. To renew its status, an ONC–ACB is required to submit a renewal request which contains any updates to the information requested in the initial application to the National Coordinator 60 days prior to the expiration of its status.
B6. How can I submit a Health IT related complaint?
Complaints can be submitted via the Health IT Complaint Form.
B7. What does the ONC Certified HIT Certification and Design Mark represent?
The ONC Certified HIT Mark Certification and Design (Mark) is available to represent products that have been certified by an ONC-ACB under the ONC Health IT Certification Program and meet the 2014 Edition or 2015 Edition Standards and Certification Criteria. This means that a product was tested in accordance with the ONC-Approved Test Method, and certified in accordance with the standards and certification criteria adopted by the Secretary and all other requirements of the ONC Health IT Certification Program.
ONC-ACBs may grant the use of the Mark (on behalf of ONC) to developers or vendors who have certified HIT under the ONC HIT Certification Program.
For more information, please see the Criteria and Terms of Use for the ONC Certified HIT Certification and Design Mark [PDF - 201 KB].
B8. What is gap certification?
Gap certification is the certification of a previously certified Complete EHR or EHR Module(s) to:
- All applicable new and/or revised certification criteria adopted by the Secretary based on the test results of an Accredited Testing Laboratory (ATL); and
- All other applicable certification criteria adopted by the Secretary based on the test results used to previously certify the Complete EHR or EHR Module(s).
B9. What happens to Health IT modules when new standards and certification criteria are released?
ONC-Authorized Certification Bodies (ONC-ACBs) may certify Complete EHRs and/or Health IT Module(s) to a newer version of certain identified minimum standards specified below if the Secretary has accepted a newer version of an adopted minimum standard.
Applicability of an accepted newer version of an adopted minimum standard:
- ONC-ACBs are not required to certify Health IT Module(s) according to newer versions of an adopted minimum standard accepted by the Secretary until the incorporation by reference provision of the adopted version is updated in the Federal Register with a newer version.
- Certified EHR Technology may be upgraded to comply with newer versions of an adopted minimum standard accepted by the Secretary without adversely affecting the certification status of the Certified EHR Technology.
B10. What is inherited certification status?
An ONC-Authorized Certification Body (ONC-ACB) must accept requests for a newer version of a previously certified Complete EHR or EHR Module(s) to inherit the certified status of the previously certified Complete EHR or EHR Module(s) without requiring the newer version to be recertified.
B11. How does inherited certification status work?
Before granting certified status to a newer version of a previously certified Complete EHR or EHR Module(s), an ONC-Authorized Certification Body (ONC-ACB) must review an attestation submitted by the developer of the Complete EHR or EHR Module(s) to determine whether any change in the newer version has adversely affected the Complete EHR's or EHR Module(s)' capabilities for which certification criteria have been adopted.
An ONC-ACB may grant certified status to a newer version of a previously certified Complete EHR or EHR Module(s) if it determines that the capabilities for which certification criteria have been adopted have not been adversely affected.
B12. How does inherited certification status work for EHR Module(s)?
An ONC-Authorized Certification Body (ONC-ACB) must accept requests for a newer version of a previously certified EHR Module(s) to inherit the certified status of the previously certified EHR Module(s) without requiring the newer version to be recertified.
- Before granting certified status to a newer version of a previously certified EHR Module(s), an ONC-ACB must review an attestation submitted by the developer(s) of the EHR Module(s) to determine whether any change in the newer version has adversely affected the EHR Module(s)' capabilities for which certification criteria have been adopted.
- An ONC-ACB may grant certified status to a newer version of a previously certified EHR Module(s) if it determines that the capabilities for which certification criteria have been adopted have not been adversely affected.
B13. How does privacy and security certification work for Health Module certification?
EHR Module(s) shall be certified to all privacy and security certification criteria adopted by the Secretary, unless the EHR Module(s) is presented for certification in one of the following manners:
- The EHR Modules are presented for certification as a pre-coordinated, integrated bundle of EHR Modules, which would otherwise meet the definition of and constitute a Complete EHR, and one or more of the constituent EHR Modules is demonstrably responsible for providing all of the privacy and security capabilities for the entire bundle of EHR Modules; or
- An EHR Module is presented for certification, and the presenter can demonstrate and provide documentation to the ONC-Authorized Certification Body (ONC-ACB) that a privacy and security certification criterion is inapplicable or that it would be technically infeasible for the EHR Module to be certified in accordance with such certification criterion.
C. Testing
C1. Where can I find the ONC-Approved Test Method?
The ONC-approved Test Method is available here.
C2. What is the role of the National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program (NVLAP)?
NVLAP, as administered by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), is responsible for accrediting and overseeing testing laboratories in the ONC HIT Certification Program.
C3. What is the role of Accredited Testing Laboratories (ATLs) in the ONC Health IT Certification Program, and how do organizations apply to become an ATL?
ATLs test products against the standards and certification criteria identified by the Secretary. Successfully tested products can be submitted to an ONC-ACB for certification and listing on the CHPL.
NVLAP is responsible for the accreditation of testing laboratories in the ONC HIT Certification Program. Instructions on how to apply to NVLAP for accreditation are included on the NVLAP website: Instructions for Completing a NVLAP Application.
C4. Where can I find a list of Accredited Testing Laboratories (ATLs)?
The list is available here.
C5. Are code sets available in the ONC Health IT Certification Program?
The ONC Health IT Certification Program calls for publishing any Secretarial determinations that have been made with respect to "minimum standard" code sets to be published regularly on a quarterly basis. If the Secretary accepts a newer version of a "minimum standard" code set, nothing is required of ONC-Authorized Certification Bodies (ONC-ACBs), Complete EHR or EHR Module developers, or the eligible professionals and eligible hospitals who have implemented Certified EHR Technology.
D. Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL)
D1. What is the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL), and where can I find a list of certified Health IT modules?
The CHPL provides the authoritative, comprehensive listing of Health IT Modules that have been tested and certified through the ONC Health IT Certification Program.
All certified Health IT modules are posted on the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL).
D2. How do I use the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL) and obtain a CMS EHR Certification ID?
Step-by-step instructions [PDF - 1.9 MB] for navigating the CHPL and obtaining a CMS EHR Certification ID are available on the CHPL website.
D3. How can I check that the electronic health record (EHR) or Health IT module that I’m using is certified, and how often is the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL) updated?
If your Health IT Module is listed on the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL), it has been certified through the ONC Health IT Certification Program. The CHPL is updated, at minimum, once per week.
D4. What should I do if I do not see my certified Health IT Module on the CHPL?
If you do not see your ONC certified Complete EHR or Health IT Module posted, please contact the ONC-Authorized Certification Body (ONC-ACB) that certified your product.
Contact information for all ONC-ACBs can be found here.
D5. What does "Additional Software Required” mean?
"Additional Software Required" includes any additional software that a certified Complete EHR or Health IT Module relied upon to demonstrate its compliance with a certification criterion or criteria adopted by the Secretary of the United States Department of Health and Human Services.
D6. What is the difference between a Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL) Product Number and a CMS EHR Certification ID?
Each certified Health IT Module on the CHPL has a “CHPL Product Number” assigned to it by the ONC-Authorized Certification Body (ONC-ACB) that certified the product. The CMS EHR Certification Identification Number is a number generated by the CHPL that represents a Health IT Module or combination of Health IT Modules, which are used for reporting EHR Incentive Programs.
D7. How do I get my Health IT Module listed on the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL)?
Health IT Modules must be tested by an Accredited Testing Laboratory (ATL) and then certified by an ONC-Authorized Certification Body (ONC-ACB) to be listed on the CHPL.
Once the product has been certified, the ONC-ACB will initiate the process to have the product listed on the CHPL.
D8. Who do I contact with questions or concerns about the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL) or if my CHPL listing is incorrect?
Developers with questions about their Certified Health IT Module should contact the ONC-Authorized Testing and Certification Body (ONC-ATCB) or ONC-Authorized Certification Body (ONC-ACB) that certified their Health IT Module.
If the ONC-ACB cannot or does not address your issue, please submit your issue via the Centralized Feedback System. Select the applicable category to enter a ticket.
E. Complaints and Violations
E1. What do I do if I have a complaint about an Accredited Testing Laboratory (ATL) and/or an ONC-Authorized Certification Body (ONC-ACB), a vendor or a product?
| Issue | Contact |
| Eligible Professionals & Eligible Hospital complaints regarding an EHR product | Please reference the Provider Complaint Process page |
| Developer complaint against an ATL or ONC-ACB | Please contact the ATL or ONC-ACB first, to resolve the issue. Complaints should be escalated to NVLAP or the ONC-AA if the issue persists. |
| Product Listing on the CHPL | Please contact the ONC-ATCB or ONC-ACB that certified the product |
| Other comments or complaints | Health IT related complaints can be submitted via the ONC Health IT Complaint form. Other comments or concerns can be submitted to the ONC Health IT Certification Program via ONC.Certification@hhs.gov. |
E2. How are violations handled in the ONC Health IT Certification Program?
There is a specific course of action for violations in the ONC HIT Certification Program. There are Type-1 and Type-2 violations, both described below, and they each have different criteria and follow-up actions.
Type-1 violations: The National Coordinator may revoke an ONC-Authorized Certification Body's (ONC-ACB) status for committing a Type-1 violation. Type-1 violations include violations of law or ONC HIT Certification Program policies that threaten or significantly undermine the integrity of the ONC HIT Certification Program. These violations include, but are not limited to: False, fraudulent, or abusive activities that affect the ONC HIT Certification Program, a program administered by HHS or any program administered by the Federal government.
Type-2 violations: The National Coordinator may revoke an ONC-ACB's status for failing to timely or adequately correct a Type-2 violation. Type-2 violations constitute noncompliance with Sec. 170.560.
- Noncompliance notification. If the National Coordinator obtains reliable evidence that an ONC-ACB may no longer be in compliance with Sec. 170.560, the National Coordinator will issue a noncompliance notification with reasons for the notification to the ONC-ACB requesting that the ONC-ACB respond to the alleged violation and correct the violation, if applicable.
- Opportunity to become compliant. After receipt of a noncompliance notification, an ONC-ACB is permitted up to 30 days to submit a written response and accompanying documentation that demonstrates that no violation occurred or that the alleged violation has been corrected.
E3. What is proposed revocation?
The National Coordinator may propose to revoke an ONC-ACB's status if the National Coordinator has reliable evidence that the ONC-ACB has committed a Type-1 violation. The National Coordinator may propose to revoke an ONC-ACB's status if, after the ONC-ACB has been notified of a Type-2 violation, the ONC-ACB fails to:
- To rebut the finding of a violation with sufficient evidence showing that the violation did not occur or that the violation has been corrected; or
- Submit to the National Coordinator a written response to the noncompliance notification within the specified timeframe.
Can’t find the answer to your question? Contact ONC Health IT Certification Program via ONC.Certification@hhs.gov.
The Temporary Certification Program FAQs have been archived here.


